Details of the Drug
General Information of Drug (ID: DMAY7H4)
| Drug Name |
Valdecoxib
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Bextra; COX; Kudeq; Valdyn; Pfizer brand of valdecoxib; Valdecoxib [USAN]; SC 65872; ND-0214; SC-65872; YM-974; Valdecoxib (USAN/INN); P-(5-Methyl-3-phenyl-4-isoxazolyl)benzenesulfonamide; Benzenesulfonamide, 4-(5-methyl-3-phenyl-4-isoxazolyl)-(9CI); 4-(5-Methyl-3-phenyl-4-isoxazolyl)benzenesulfonamide; 4-(5-methyl-3-phenyl-1,2-oxazol-4-yl)benzenesulfonamide; 4-(5-methyl-3-phenyl-4-isoxazolyl) benzenesulfonamide; 4-(5-methyl-3-phenyl-isoxazol-4-yl)benzenesulfonamide; 4-(5-methyl-3-phenylisoxazol-4-yl)benzenesulfonamide; 4-(Methyl-3-phenyl-isoxazol-4-yl)-benzenesulfonamide
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indication |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Therapeutic Class |
Antiinflammatory Agents
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Affected Organisms |
Humans and other mammals
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| ATC Code | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure |
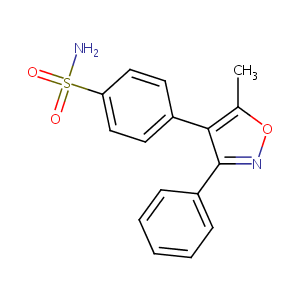 |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D MOL | 2D MOL | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| #Ro5 Violations (Lipinski): 0 | Molecular Weight (mw) | 314.4 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Logarithm of the Partition Coefficient (xlogp) | 2.6 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) | 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) | 5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| ADMET Property |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Identifiers |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cross-matching ID | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Interaction Atlas of This Drug
 Drug Therapeutic Target (DTT) |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Drug-Metabolizing Enzyme (DME) |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Drug Off-Target (DOT) |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Interaction Atlas (MIA) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Expression Atlas of This Drug
| The Studied Disease | Osteoarthritis | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ICD Disease Classification | FA00-FA05 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Expression Atlas (MEA) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Experimental Cancer Drug Sensitivity Information
Drug-Drug Interaction (DDI) Information of This Drug
|
Coadministration of a Drug Treating the Same Disease as Valdecoxib
Coadministration of a Drug Treating the Disease Different from Valdecoxib (Comorbidity)
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
References
| 1 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 2894). | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | BDDCS applied to over 900 drugs | ||||
| 3 | Trend Analysis of a Database of Intravenous Pharmacokinetic Parameters in Humans for 1352 Drug Compounds | ||||
| 4 | Estimating the safe starting dose in phase I clinical trials and no observed effect level based on QSAR modeling of the human maximum recommended daily dose | ||||
| 5 | Biochemical mechanisms of New Molecular Entities (NMEs) approved by United States FDA during 2001-2004: mechanisms leading to optimal efficacy and ... Curr Top Med Chem. 2006;6(5):461-78. | ||||
| 6 | Simultaneous assessment of drug interactions with low- and high-extraction opioids: application to parecoxib effects on the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of fentanyl and alfentanil. Anesthesiology. 2003 Apr;98(4):853-61. | ||||
| 7 | Genetically based impairment in CYP2C8- and CYP2C9-dependent NSAID metabolism as a risk factor for gastrointestinal bleeding: is a combination of pharmacogenomics and metabolomics required to improve personalized medicine? Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2009 Jun;5(6):607-20. | ||||
| 8 | Substrates, inducers, inhibitors and structure-activity relationships of human Cytochrome P450 2C9 and implications in drug development. Curr Med Chem. 2009;16(27):3480-675. | ||||
| 9 | Association of CYP1A1 and CYP1B1 inhibition in in vitro assays with drug-induced liver injury. J Toxicol Sci. 2021;46(4):167-176. doi: 10.2131/jts.46.167. | ||||
| 10 | The effect of valdecoxib on the production of growth factors evoked by hypoxia and bacterial lipopolysaccharide in HMEC-1 cells. Adv Clin Exp Med. 2013 Nov-Dec;22(6):795-800. | ||||
| 11 | Systems pharmacological analysis of drugs inducing stevens-johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis. Chem Res Toxicol. 2015 May 18;28(5):927-34. doi: 10.1021/tx5005248. Epub 2015 Apr 3. | ||||
| 12 | The effect of mild and moderate hepatic impairment on the pharmacokinetics of valdecoxib, a selective COX-2 inhibitor. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2005 Jun;61(4):247-56. | ||||
| 13 | Product Information. Solaraze (diclofenac topical). Doak Dermatologics Division, Fairfield, NJ. | ||||
| 14 | Cerner Multum, Inc. "Australian Product Information.". | ||||
| 15 | Abad S, Moachon L, Blanche P, Bavoux F, Sicard D, Salmon-Ceron D "Possible interaction between glicazide, fluconazole and sulfamethoxazole resulting in severe hypoglycaemia." Br J Clin Pharmacol 52 (2001): 456-7. [PMID: 11678792] | ||||
| 16 | Christensen LK, Hansen JM, Kristensen M "Sulphaphenazole-induced hypoglycemic attacks in tolbutamide-treated diabetics." Lancet 2 (1963): 1298-301. [PMID: 14071924] | ||||
| 17 | Cerner Multum, Inc. "UK Summary of Product Characteristics.". | ||||
| 18 | Product Information. Bextra (valdecoxib). Pharmacia Corporation, Peapack, NJ. | ||||
| 19 | Product Information. Multaq (dronedarone). sanofi-aventis , Bridgewater, NJ. | ||||
| 20 | Product Information. Sirturo (bedaquiline). Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Titusville, NJ. | ||||
| 21 | Buchman AL, Schwartz MR "Colonic ulceration associated with the systemic use of nonsteroidal antiinflammatory medication." J Clin Gastroenterol 22 (1996): 224-6. [PMID: 8724264] | ||||
| 22 | Product Information. Factive (gemifloxacin). GeneSoft Inc, San Francisco, CA. | ||||
| 23 | Assael BM, Chiabrando C, Gagliardi L, Noseda A, Bamonte F, Salmona M "Prostaglandins and aminoglycoside nephrotoxicity." Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 78 (1985): 386-94. [PMID: 4049389] | ||||
| 24 | Davey PG "Overview of drug interactions with the quinolones." J Antimicrob Chemother 22(suppl c) (1988): 97-107. [PMID: 3053579] | ||||
| 25 | Product Information. Ketek (telithromycin). Aventis Pharmaceuticals, Bridgewater, NJ. | ||||
| 26 | Product Information. Actonel (risedronate). Procter and Gamble Pharmaceuticals, Cincinnati, OH. | ||||
| 27 | Product Information. Turalio (pexidartinib). Daiichi Sankyo, Inc., Parsippany, NJ. | ||||
| 28 | Fuhr U, Maier-Bruggemann A, Blume H, et al. "Grapefruit juice increases oral nimodipine bioavailability." Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther 36 (1998): 126-32. [PMID: 9562227] | ||||
| 29 | Product Information. Yasmin (drospirenone-ethinyl estradiol) Berlex Laboratories, Richmond, CA. | ||||
| 30 | Product Information. Korlym (mifepristone). Corcept Therapeutics Incorporated, Menlo Park, CA. | ||||
| 31 | Product Information. Kalydeco (ivacaftor). Vertex Pharmaceuticals, Cambridge, MA. | ||||
| 32 | Product Information. Prevymis (letermovir). Merck & Company Inc, Whitehouse Station, NJ. | ||||
| 33 | Product Information. Emend (aprepitant). Merck & Company Inc, West Point, PA. | ||||
| 34 | Muller FO, Schall R, Devaal AC, Groenewoud G, Hundt HKL, Middle MV "Influence of meloxicam on furosemide pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics in healthy volunteers." Eur J Clin Pharmacol 48 (1995): 247-51. [PMID: 7589049] | ||||
| 35 | Abdel-Haq B, Magagna A, Favilla S, Salvetti A "Hemodynamic and humoral interactions between perindopril and indomethacin in essential hypertensive subjects." J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 18 (1991): s33-6. [PMID: 1725198] | ||||
| 36 | Product Information. Priftin (rifapentine). Hoechst Marion-Roussel Inc, Kansas City, MO. | ||||
| 37 | Product Information. Adcetris (brentuximab vedotin). Seattle Genetics Inc, Bothell, WA. | ||||
| 38 | Product Information. Sustiva (efavirenz). DuPont Pharmaceuticals, Wilmington, DE. | ||||
| 39 | Product Information. Prezista (darunavir). Ortho Biotech Inc, Bridgewater, NJ. | ||||
| 40 | Product Information. Kynamro (mipomersen). Genzyme Corporation, Cambridge, MA. | ||||
| 41 | EMEA "EMEA public statement on leflunomide (ARAVA) - severe and serious hepatic reactions.". | ||||
| 42 | Product Information. Juxtapid (lomitapide). Aegerion Pharmaceuticals Inc, Cambridge, MA. | ||||
| 43 | McCarthy JT, Torres VE, Romero JC, et al "Acute intrinsic renal failure induced by indomethacin." Mayo Clin Proc 57 (1982): 289-96. [PMID: 6952058] | ||||
| 44 | Product Information. Vaprisol (conivaptan). Cumberland Pharmaceuticals Inc, Nashville, TN. | ||||
| 45 | Novis BH, Korzets Z, Chen P, Bernheim J "Nephrotic syndrome after treatment with 5-aminosalicylic acid." Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 296 (1988): 1442. [PMID: 3132281] | ||||
| 46 | Product Information. Alunbrig (brigatinib). Ariad Pharmaceuticals Inc, Cambridge, MA. | ||||
| 47 | Product Information. Lorbrena (lorlatinib). Pfizer U.S. Pharmaceuticals Group, New York, NY. | ||||
| 48 | Product Information. Retevmo (selpercatinib). Lilly, Eli and Company, Indianapolis, IN. | ||||
| 49 | Al-Nawakil C, Willems L, Mauprivez C, et.al "Successful treatment of l-asparaginase-induced severe acute hepatotoxicity using mitochondrial cofactors." Leuk Lymphoma 55 (2014): 1670-4. [PMID: 24090500] | ||||
| 50 | Product Information. Zydelig (idelalisib). Gilead Sciences, Foster City, CA. | ||||
| 51 | Product Information. Copiktra (duvelisib). Verastem, Inc., Needham, MA. | ||||
| 52 | Bailey DG, Arnold JMO, Spence JD "Grapefruit juice and drugs - how significant is the interaction." Clin Pharmacokinet 26 (1994): 91-8. [PMID: 8162660] | ||||
| 53 | Product Information. Exjade (deferasirox). Novartis Pharmaceuticals, East Hanover, NJ. | ||||
| 54 | Product Information. Tasigna (nilotinib). Novartis Pharmaceuticals, East Hanover, NJ. | ||||
| 55 | Product Information. Sprycel (dasatinib). Bristol-Myers Squibb, Princeton, NJ. | ||||
| 56 | Doherty MM, Charman WN "The mucosa of the small intestine: how clinically relevant as an organ of drug metabolism?" Clin Pharmacokinet 41 (2002): 235-53. [PMID: 11978143] | ||||
| 57 | EMA. European Medicines Agency. European Union "EMA - List of medicines under additional monitoring.". | ||||
| 58 | Abdel-Rahman MS, Reddi AS, Curro FA, Turkall RM, Kadry AM, Hansrote JA "Bioavailability of aspirin and salicylamide following oral co-administration in human volunteers." Can J Physiol Pharmacol 69 (1991): 1436-42. [PMID: 1777842] | ||||
| 59 | Product Information. Xeglyze (abametapir topical). Dr. Reddy's Laboratories Inc, Upper Saddle River, NJ. | ||||
| 60 | Product Information. Xenleta (lefamulin). Nabriva Therapeutics US, Inc., King of Prussia, PA. | ||||
| 61 | Product Information. Zokinvy (lonafarnib). Eiger BioPharmaceuticals, Palo Alto, CA. | ||||
| 62 | Benoist G, van Oort I, et al "Drug-drug interaction potential in men treated with enzalutamide: Mind the gap." Br J Clin Pharmacol 0 (2017): epub. [PMID: 28881501] | ||||
| 63 | Product Information. Prograf (tacrolimus). Fujisawa, Deerfield, IL. | ||||
| 64 | DSouza DL, Levasseur LM, Nezamis J, Robbins DK, Simms L, Koch KM "Effect of alosetron on the pharmacokinetics of alprazolam." J Clin Pharmacol 41 (2001): 452-4. [PMID: 11304902] | ||||
| 65 | Product Information. ReVia (naltrexone). DuPont Pharmaceuticals, Wilmington, DE. | ||||
| 66 | Product Information. Tavalisse (fostamatinib). Rigel Pharmaceuticals, South San Francisco, CA. | ||||
| 67 | Farag MM, Mikhail MR, Abdel-Meguid E, Abdel-Tawab S "Assessment of gentamicin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats treated with low doses of ibuprofen and diclofenac sodium." Clin Sci 91 (1996): 187-91. [PMID: 8795442] | ||||
